🔍 How Laravel Works: A Deep Dive into MVC Functionality
Laravel is one of the most powerful and developer-friendly PHP frameworks available today. Its clean syntax, built-in tools, and modular structure make it a go-to choice for web applications.
But how does Laravel actually work behind the scenes?
In this article, we'll explore the core functionality of Laravel through the lens of the MVC (Model-View-Controller) architecture.
🧱 What is MVC?
MVC is a software design pattern that separates an application into three main components:
- Model – Handles data and database operations.
- View – Manages the user interface and presentation.
- Controller – Acts as a middle layer between models and views, handling user input and application logic.
Laravel follows this architecture to ensure code organization, reusability, and scalability.
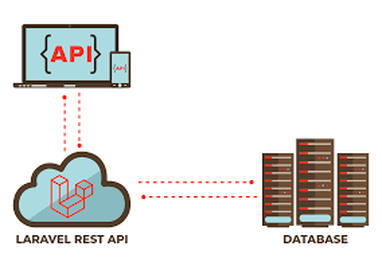
🚦 1. The Request Lifecycle in Laravel
Before diving into MVC, it’s important to understand how Laravel handles a request:
- User hits a URL in the browser.
- The request is captured by Laravel’s
public/index.phpfile. - Laravel boots up, loading service providers and configurations.
- The request is passed to the router.
- The router directs the request to the appropriate controller method.
- The controller may use a model to interact with the database.
- The controller returns a view (or JSON/API response).
- The browser receives and displays the response.
🗂️ How Each Layer Works in Laravel
1️⃣ Model: The Data Layer
In Laravel, models are PHP classes that represent database tables. They use Eloquent ORM, Laravel's built-in Object-Relational Mapping system.
Example:
class Post extends Model
{
protected $fillable = ['title', 'content'];
}This allows you to interact with the posts table using simple syntax:
Post::create(['title' => 'Laravel Rocks', 'content' => 'Here is why...']);Laravel automatically connects models to tables by naming convention. Post → posts.
2️⃣ Controller: The Logic Layer
Controllers handle user input, process data, and return a response.
Example:
class PostController extends Controller
{
public function index()
{
$posts = Post::all();
return view('posts.index', compact('posts'));
}
}Controllers sit between the route and the model, keeping logic clean and centralized.
3️⃣ View: The Presentation Layer
Views are Blade templates located in the resources/views directory. They handle how the data is presented to users.
Example: resources/views/posts/index.blade.php
@foreach ($posts as $post)
<h2>{{ $post->title }}</h2>
<p>{{ $post->content }}</p>
@endforeachLaravel's Blade templating engine allows you to write PHP inside HTML using elegant syntax ({{ }} and @directives).
🧭 Routing: The Traffic Controller
Routes are defined in routes/web.php and tell Laravel which controller to call for a given URL.
Route::get('/posts', [PostController::class, 'index']);
When a user visits /posts, Laravel calls the index method in PostController.
🧠 Behind the Scenes
Here’s what happens step-by-step when a user visits /posts:
- Route match: Laravel finds a route in
web.php. - Controller call: It invokes the
indexmethod inPostController. - Model fetch: The controller uses the
Postmodel to get data from the database. - View render: The controller passes data to a Blade view.
- Response sent: The view is compiled into HTML and sent to the browser.
⚙️ Other Core Laravel Functionalities
Laravel is much more than just MVC. It also includes:
- 🔐 Middleware – For handling authentication, CORS, etc.
- 🎯 Dependency Injection – For automatic object resolution.
- 📨 Request Validation – For secure data handling.
- 📦 Service Providers – For bootstrapping services.
- 🔄 Queues, Jobs, Events – For asynchronous workflows.
✅ Conclusion
Laravel's use of MVC architecture helps developers build web applications that are clean, organized, and maintainable. By separating logic (Controller), data (Model), and presentation (View), Laravel makes it easier to scale and manage complex applications.
Understanding the Laravel request lifecycle and how MVC fits into it is the first step toward mastering this powerful PHP framework.
💡 Want to Go Further?
- Build a CRUD app using MVC.
- Add authentication using Laravel Breeze or Jetstream.
- Dive into advanced features like APIs, Livewire, or queues.

I'm a dedicated full-stack developer with expertise in building and managing dynamic web applications across both frontend and backend.